The West's terminal technology problem
Western powers are falling behind in technology, held back by systemic rot
Western powers are falling behind in the development of new technologies, particularly in the military domain. This is partly caused by the perverse system of incentives that suffocates research and development work, but also by a system of education that’s producing less and less technical, scientific and engineering talent. From the strategic point of view, this is a critical problem, as I elaborated in an earlier Substack, “Of Empires and Technology.”
Russia has eclipsed the West in military technology
At the 8th Eastern Economic Forum held earlier this month in Vladivostok, Russia's President Vladimir Putin spoke about the development of a new generation of weapons: "If one looks into the security sphere, new physical principles weapons will ensure the security of any country in the near historic perspective. We understand this very well and are working on it."
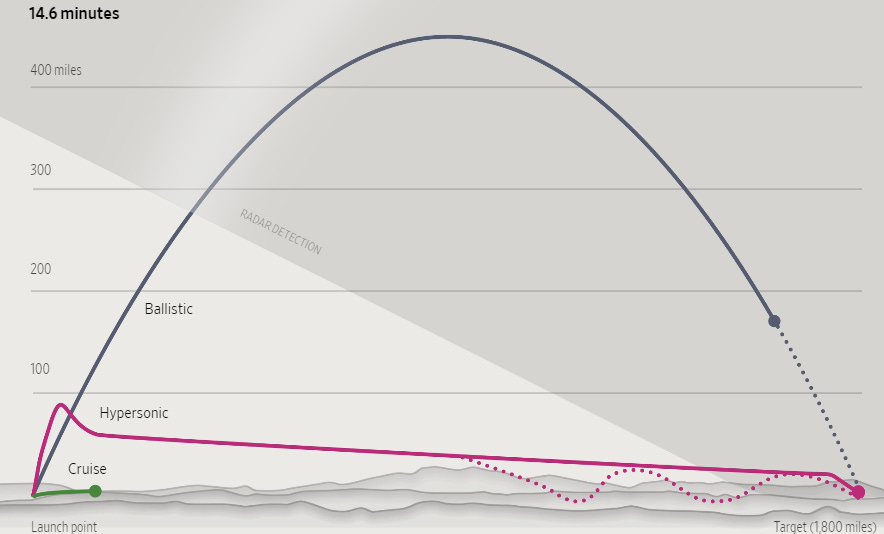
The kinds of weapons Putin was referring to include particle beams, laser, ultrasonic, radio-frequency and electromagnetic systems. That sounds quite futuristic - was Putin telling tall tales? When he announced that Russia had developed a variety of undetectable hypersonic weapons back in 2018, many in the West thought that he was bluffing and we heard much mocking and crowing: "the West outspends Russia 10 to 1, the Russians can't possibly bla, bla, bla..." And like the Chinese, the Russians are inferior and incapable of innovating, they can't think strategically, etc.
Fast forward to today: the Russian forces have successfully deployed hypersonic Kinzhal and Zircon missiles in Ukraine, delivering pinpoint strikes on Ukrainian infrastructure and military facilities, the crowing and the gloating about all the ways in which the Russians are inferior to us westerners has died down a bit. Still, we can’t just admit that Russian weapons systems are superior to the western arsenal, so the western press, relying on Ukrainian sources, claimed that Ukraine's air defenses manage to intercept and shoot down Russian hypersonic missiles.
That would actually quite spectacular since NATO officials themselves have corroborated what Putin had said: that the missiles are undetectable and were not picked up by western radar systems. Either the Ukrainians have managed to develop targeting solutions very fast, using binoculars, or they're lying. Whatever the case, Putin’s latest announcement did not trigger much mocking and crowing this time around. In fact, some western analysts now concede that Russia's military technology has eclipsed that of the west.
The significance of hypersonic weapons
But how can this even be possible if for decades now, western "defense" spending outstripped that of Russia by a factor of 10 or even more? In a recent article titled, "Hypersonic Missiles Are Game-Changers, and America Doesn't Have Them," the Wall Street Journal explored why the US and the West have fallen behind.
"For more than 60 years," says WSJ, "the U.S. has invested billions of dollars in dozens of programs to develop its own version of the [hypersonic weapons] technology. Those efforts have either ended in failure or have been cancelled before having a chance to succeed. ... This situation is raising alarms."
Last March I explained why hypersonics are a radical game-changer in my Substack article titled, "Why hypersonic weapons change everything". Indeed, hypersonic systems are regarded as so critical that in 2021, US National Defense Authorization Act explicitly made the development of these systems a priority in US defense spending.
Meanwhile, Wall Street Journal didn’t provide any convincing explanation for why western powers are falling behind in development of new technologies. It also didn’t explore the fact that they even fall behind in production and maintenance of legacy systems. As NATO's Admiral Robert Bauer lamented this week,
"Today the chiefs of defense expressed their concern that across the alliance, production capacity is lagging behind. Delivery times are moving to the right [they're getting longer] and prices for equipment and ammunition are shooting up. Right now we are paying more and more for exactly the same, and that means that we cannot make sure that the increased defense spending actually leads to more security."
Bauer's statement is a clear admission that defense spending does not translate into better defense. He also said that, "Our liberal economies are not apt at creating the prioritization that is so desperately needed right now."
The problem with incentives
There is a great deal to ponder in all this, but it is perhaps Admiral Bauer's last statement that provides the most food for thought. Western powers do spend massively on the military, but most of that money is squandered, lubricating the wheels of corruption in the Military Industrial Complex (MIC). Spending the money (i.e. allocating it to defense contractors), is much more important than actually developing new systems and the upkeep of legacy systems.
In the United States, the MIC consists of publicly traded corporations whose market value is determined by how profitable they are. Today, about half of the Defense Department's (DOD) $850+ billion budget is spent with the DOD's top five "prime contractors" who, after decades of consolidation have all but eliminated all competition (in the 1990s the DOD had more than 50 such "prime contractors").
Given that research and development (R&D) is a cost which cuts into profitability of these very powerful contractors, they’re incentivized to reduce it as much as possible to maximize the profiteering. The more profits, the higher the stock price and the higher the executives’ bonuses. On the other hand, cutting the R&D and skimping on the essential work of technology development means that a lot of real talent and promising projects get axed even as massive pork-barrel programs like Lockheed Martin's F35 Joint Strike Fighter drain trillions of taxpayer funds. The F35 is now more than 15 years behind schedule and for its $1.7 trillion in expenditure, the program has delivered no meaningful military advantage.
Meanwhile, the lobbying arm of the MIC makes sure that such spending remains protected behind the flag and a veil of patriotism. Military generals who go along are rewarded and those who challenge the system get sidelined. That is how our wonderful "democratic system" sources top talent and delivers bestest solutions. The problem is that the top talent it draws are MBAs, lawyers and lobbyists, not scientists, engineers and systems developers. The actual military capabilities of the United States only receive lip service necessary to keep the American public distracted and unable to identify the root of the problem which is corroding the competitiveness of American industries in a very real way.
Losing talent
However, there may be deeper problems blunting the West’s technology edge, including education and cultivation of skills that are required for the challenge. Today, fewer than 20% of Americans choose STEM degrees in universities (STEM stands for Science, Technology, Engineering and Math) as more and more talent gravitates toward law and business degrees or humanities like gender studies.
According to the UNESCO, in countries like Tunisia and Malaysia as many as 37.9% and 43.5% of students (respectively), choose STEM degrees. In Germany, UAE, Belarus and India about 35% of students choose STEM degrees. While it's true that western nations can overcome the shortage of human potential by attracting foreign talent, more and more nations today offer great career opportunities and compelling work to young professionals, so western nations face tougher competition for talent.
Ignorance is strength?
There's also the problem of rigor in education, which has gone very loose in the West, and it is even affecting the prevailing cultural environment. Today for example, if you say that there are only two genders, your career could be finished that day. But if you insist that feelings matter more than facts and that 2+2 = 5, you could have a stellar career and Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation might even fund your cause with tens of millions of dollars. Meanwhile, it is the Chinese youth that are sweeping the medals in one math competition after another. They may not know how to count genders, but they seem better prepared to solve practical problems.
The problem with going fast…
Paradoxically, even technology itself may have contributed to the slowing of progress in the west through the ubiquity of software tools that make problem solving much easier than it used to be. I recently came across this little chart on social media. I must say, I felt the sting of its message personally:
When I was in high school in Croatia, our training in mathematics and science was very extensive: we had 9 hours of math per week and 6 hours of physics in addition to chemistry, biology, information technologies, software programming and more. It was a lot of work - so much so that when I came to the United States and enrolled in AP (advanced placement) math as a high school senior, I found the program very easy and aced it without even trying very hard.
By today however, I'm definitely at the "spreadsheet" stage of life: without Excel I think I'd be lost and I fear that my own conceptual thinking abilities and math problem solving skills have atrophied disconcertingly. In the west, where fast and efficient problem solving is prized over conceptual thinking and inventiveness, more and more scientists and engineers work in that last, "spreadsheet" phase, quickly working out solutions to problems, perhaps at the expense of more creative, conceptual "out of the box" thinking.
The importance of pencil-and-paper work
In places like Russia and China, that broad-based thinking and working with pencil and paper is still very much prized and their educational institutions continue to insist on it (or at least have done so in the recent past). Of course, it would be difficult to assess how creative Russian or Chinese engineers or software developers are compared to their western counterparts, but beyond leapfrogging the west in development of hypersonic weapons, I came across an interesting case that speaks to this gap.
Namely, in 2009 Goldman Sachs pressed charges for theft of intellectual property against one of their software developers, a Russian man named Sergey Aleynikov. In 2013, Michael Lewis wrote a fascinating story about that case in Vanity Fair in which he revealed that more than half of Goldman Sachs' software developers were Russian - an extremely interesting bit of information, especially in view of the notorious rigor which Goldmans is known to apply in recruiting their quants and software engineers.
Now, given that Russian software engineers don't constitute half the population of the US, either Goldman Sachs liked to have a lot of Russians lurking around, or it could be that they found them better prepared to tackle tough problem solving. The latter possibility might also explain Russia's ability to develop the Zircons, Kinzhals and Avantgard missiles as well as weapons based on new physical principles. Here's how Aleynikov himself explained the difference between Russian and American education:
“In Russia, time on the computer was measured in minutes,” he says. “When you write a program, you are given a tiny time slot to make it work. Consequently we learned to write the code in a way that minimized the amount of debugging. And so you had to think about it a lot before you committed it to paper. . . . The ready availability of computer time creates this mode of working where you just have an idea and type it and maybe erase it 10 times. Good Russian programmers, they tend to have had that one experience at some time in the past: the experience of limited access to computer time.”
Indeed, clicking "run," then deleting and retyping code is no substitute for doing a lot of thinking, which is absolutely indispensable to building high quality, reliable solutions and genuinely useful innovations.
My own experience with ‘pencil-and-paper’ R&D
My own experience in developing the I-System trading model confirmed its importance. In 1999, when my team and I built the model's prototype, it turned out to be a maintenance nightmare and it was clear that I needed to hire serious software talent to turn the prototype into a reliable tool. For a few months in 1999 I worked with an American software engineer, David B., who had recently graduated from Stanford University. Although David was extremely bright, he was literally working in the debug mode almost nonstop.
He was able to maintain the software and fix bugs as they crept up, but the code itself was growing into a patchwork of fixes and workarounds. I began to worry that sooner or later it would become unmaintainable and in 2000 I decided to hire an older engineer from Croatia, Boris Brec. Boris was old school and he insisted on extensive pencil-and-paper foundation work. He pretty much told me that he wouldn't lift a finger until I had drafted the full set of specifications explaining exactly how the model worked, including schematic process-flow drawings of all the routines under the model's hood.

The process of upgrading the I-System from the prototype to its 'industrial' version was extraordinarily labor-intensive, costly, and it took four years to complete. That was the cost of quality, which included the tradeoff between diving headlong into trading and continuing with the fastidious development work, going over every algorithm with a fine tooth-comb and testing everything ad nauseum. I was only able to do this because I managed to wrest full control and ownership over the project from my superiors.
Had the costs of project's development impacted someone's bonus, the firm’s profitability or market cap, it would have been axed and never lived to see its upgraded version. Fighting to keep the project alive and adequatly funded was a struggle at every turn. For me it is easy to see how frequently great and promising projects must die over money, missed deadlines and organizational politics.
Quality solutions, breakthroughs require abundant time and resources
The difference between I-System’s prototype and the upgrade was the change from nonstop maintenance patchwork with David to the flawlessly functioning, zero-maintenance machine put together by Boris. It was worth the four years and every euro spent on it: quality is the gift that keeps on giving, not only in having the system that functions as intended, glitch free for 20 years, but also in having the peace of mind, never fearing whether all the patchwork maintenance introduced new hidden bugs into the edifice.
The experience has taught me that this kind of work MUST begin with pencil and paper, that it must be methodical, that it must be given adequate time and resources, and that if we want to achieve quality solutions we must be willing to bear the associated costs. Where the system of incentives generates pressures to cut corners, take shortcuts and rush out half-baked solutions, it will ultimately suffocate creative work and kill many quality solutions before they had the chance to prove their merit.
Programs like supersonic weapons are only symptoms of self-inflicted systemic headwinds that are now slowing the advancements of science and technology in the Western world. A reform – nay, an overhaul of the system – will have to look at those perverse incentives as well as our educational and governance systems. This won’t be easy, especially as the western nations have deliberately seeded their political and academic structures with ideologues and zealots who are far too busy policing social justice, hate speech and gender equality to worry about the real future challenges faced by our societies.
Alex Krainer – @NakedHedgie is the creator of I-System Trend Following and publisher of daily TrendCompass investor reports which cover over 200 financial and commodities markets. One-month test drive is always free of charge, no jumping through hoops to cancel. To start your trial subscription, drop us an email at TrendCompass@ISystem-TF.com
For US investors, we propose a trend-driven inflation/recession resilient portfolio covering a basket of 30+ financial and commodities markets. For more information, you can drop me a comment or an email to xela.reniark@gmail.com





I am a pensioner with five different professions, refrigeration technician, electrical mechanic, fine instrument technician, household appliance technician and welder. I had my own business for 35 years, sometimes with 20-30 employees. I think I have quite a lot of experience. I see that the fundamental problem between the developed West and the East, mocked as backward, is that the West became comfortable, it did not have to deal with any problem solving, as it received ready-made complete units for repairs, while the "stupid" East had nothing, the components had to be taken apart the fault had to be found and repaired, since the mechanic was paid for the working units.
Miracles had to be performed every day !
In the West, if a car's transmission breaks down, the complete unit is replaced, while in the East, it is quite normal for the mechanic to disassemble the transmission and repair, say, the faulty bearing. Does anyone know a western car mechanic who can take apart a gearbox, identify the fault and repair it ? :) Show me ! :) If so, then it is a newly immigrated Eastern European or, say, an Afghan !
What we have now in the West (respect for the few exceptions) is not a professional job, but an apprentice or assistant worker !
I heard a story that in 1993 a US military radar broke down in Hungary and a " committee " from overseas came to determine the fault and order the complete :) faulty unit for the repair technicians. Well, a Hungarian technician, who once served in the army of the Warsaw Pact, identified the error in half an hour and repaired it with a few dollars worth of electronic parts bought in a shop similar to Radio Schack in the local Hungarian town ! The Americans told him that he was a genius, to which he replied that it was just a daily routine job, since he had enough practice repairing Russian radars ! :)
Great article! I totally agree with it, as I am engineer/scientist and I can relate.
I think you may like the first and latest article of Gaius Baltar’s Substack on the same topic, if you have not read them already:
- https://gaiusbaltar.substack.com/p/why-is-the-west-so-weak-and-russia
- https://gaiusbaltar.substack.com/p/what-is-wrong-with-the-western-political
Regarding R&D specifically, nowadays people tend to forget about the so-called "Project management triangle": Time - Cost - Quality.
Today everyone wants a product that it is good, cheap to build and they want it NOW.
Sorry, that is not how things work: you can only choose two - it is either:
- cheap and good, but it will take time to build;
- fast to build and good, but it will not be cheap;
- fast to build and cheap, but it will not be good (probably the worst option!).
Somehow the West, especially the US, has managed to do even worse that option 3: nowadays they develop things that are expensive, take a long time to develop and won't work - see the Bradley fighting vehicle (they even wrote a book and made a movie on it: "The Pentagon Wars").
P.S.: Keep up the good work! :)